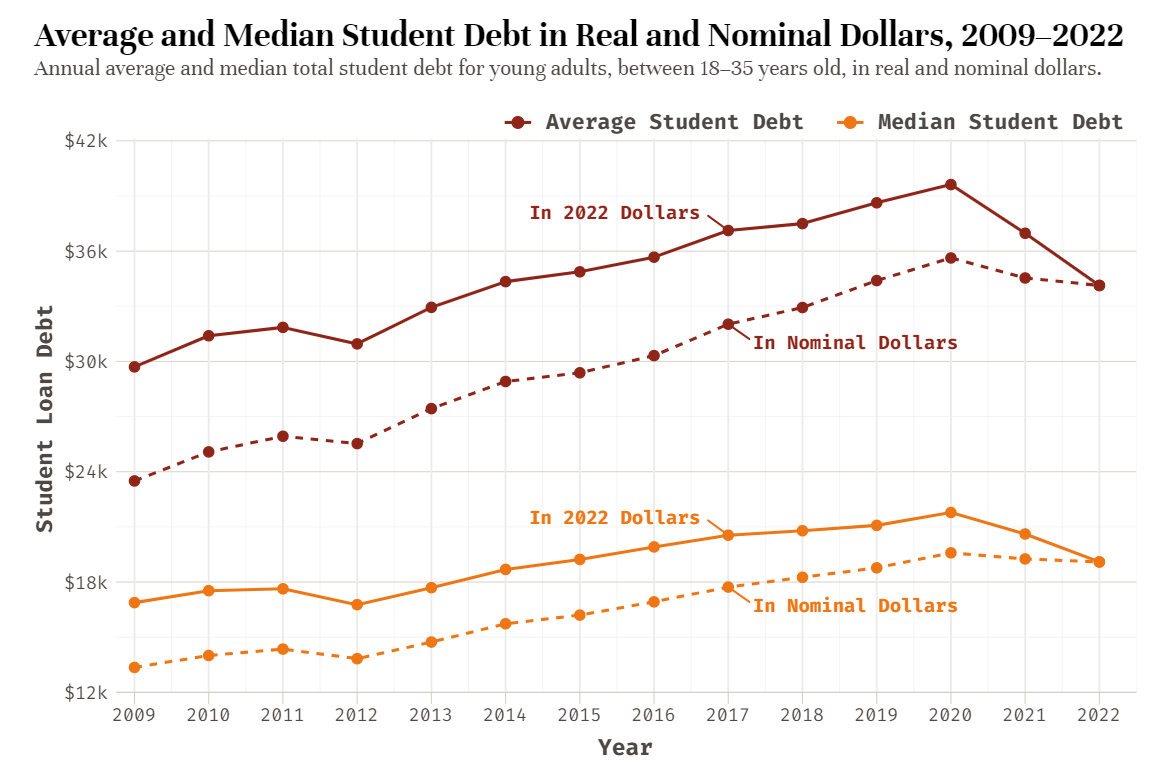
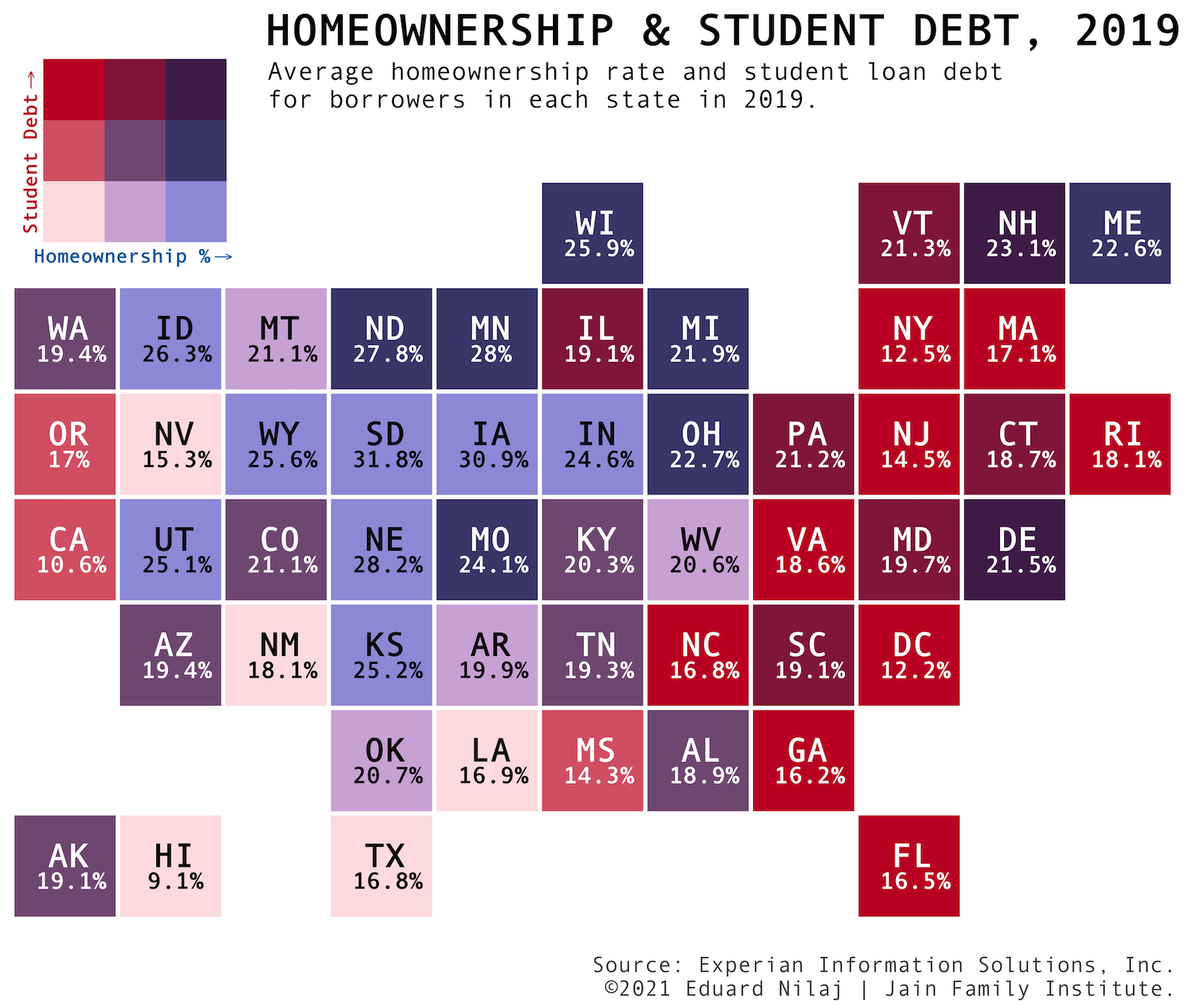
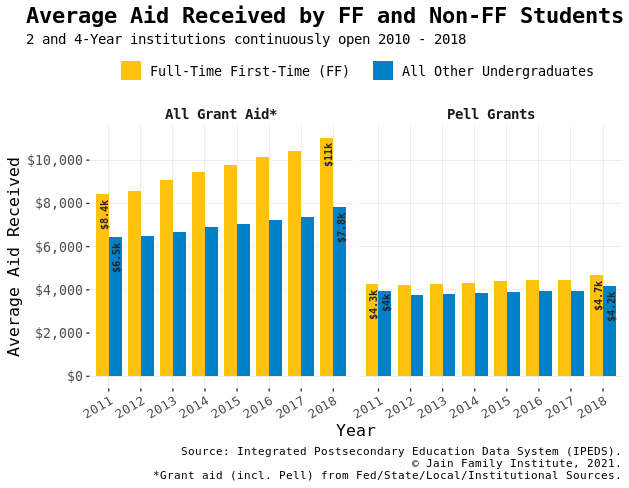
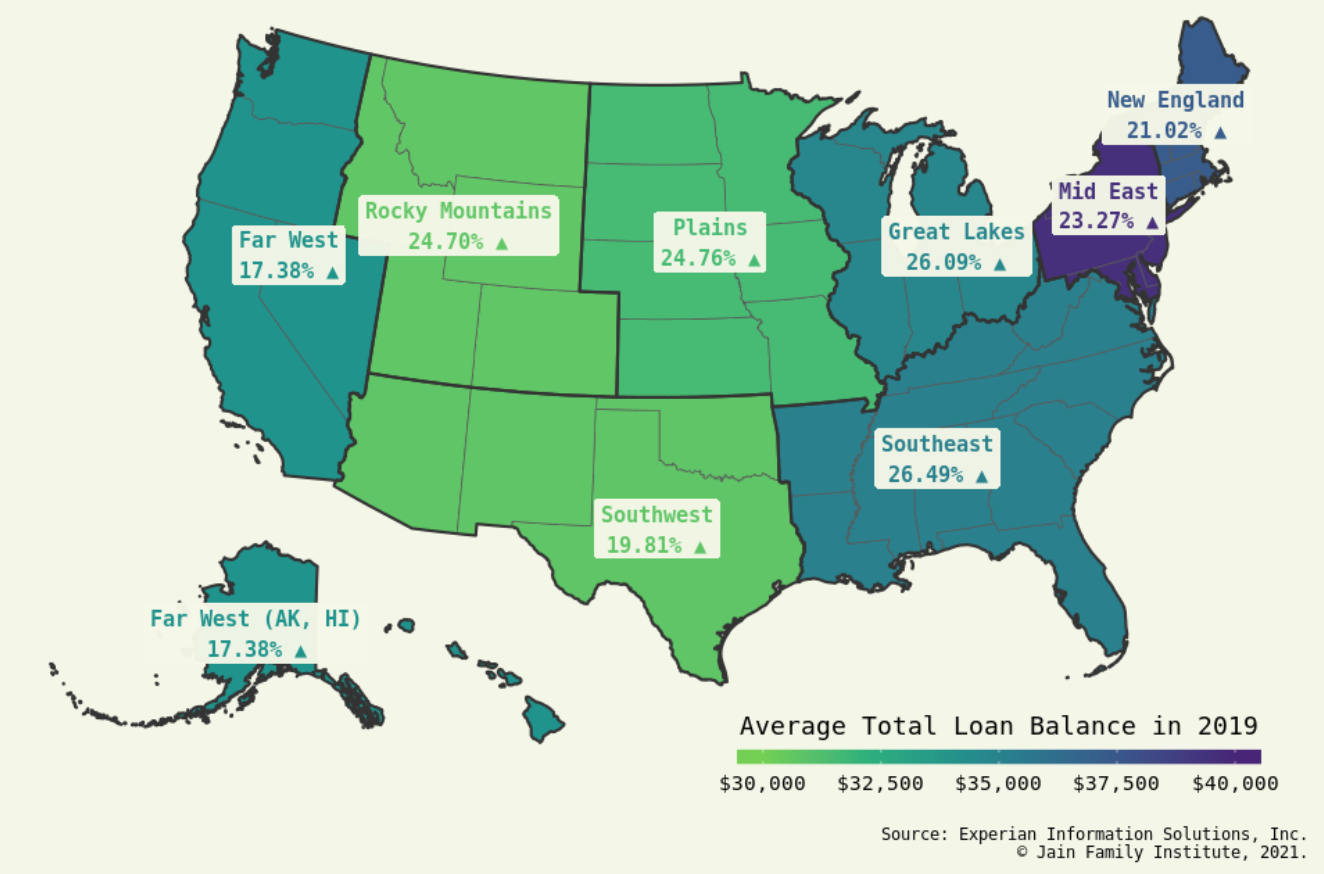
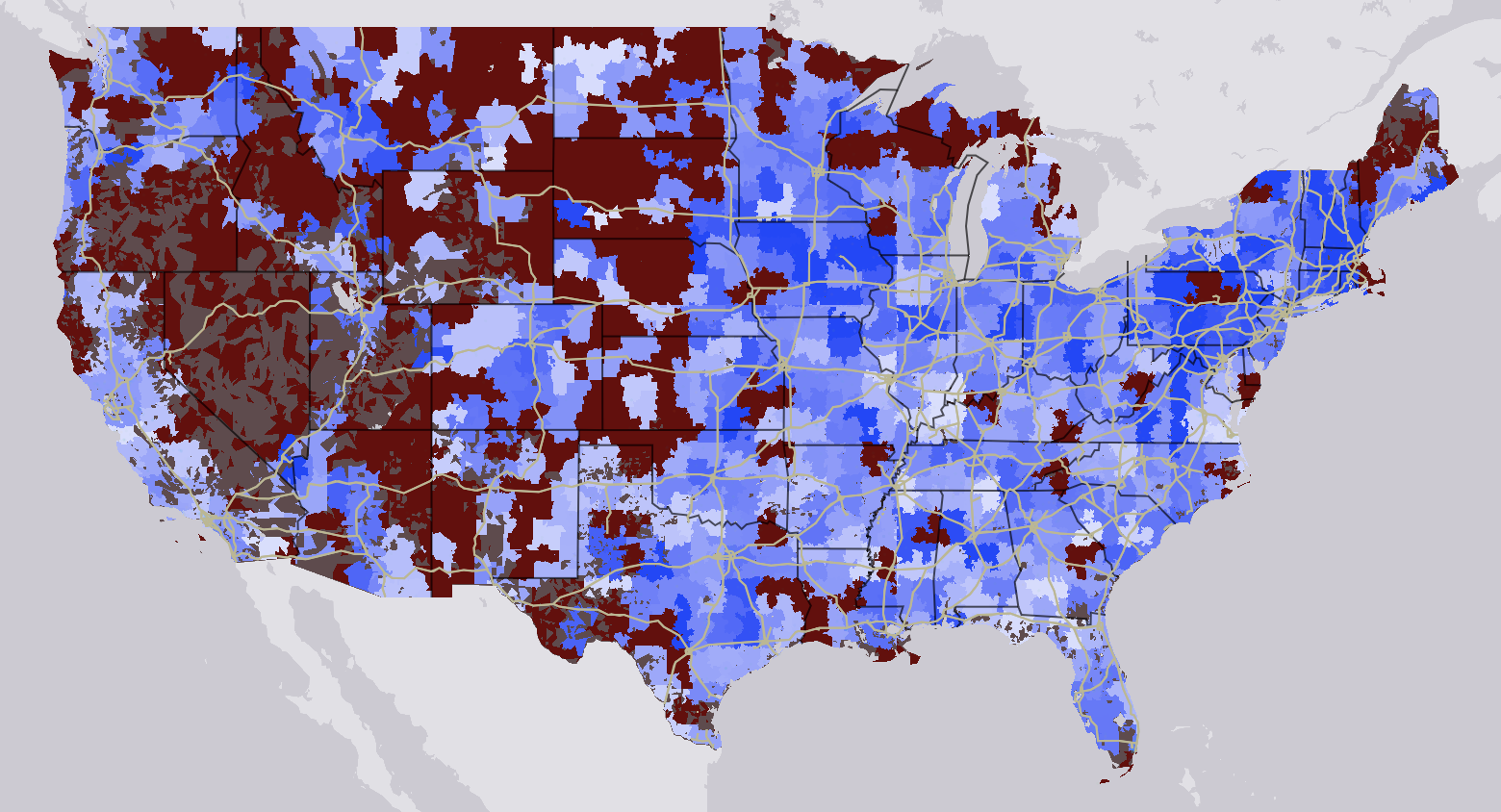
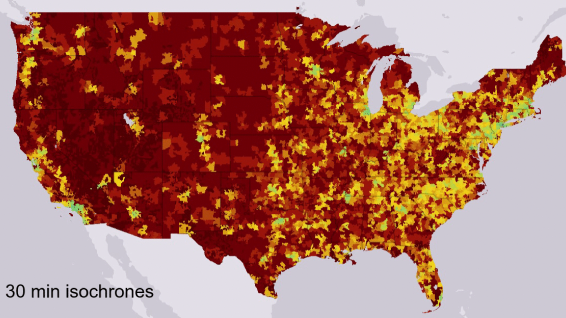
Millennial Student Debt
The Millennial Student Debt study aims to present a country-wide analysis and visualization of student debt and its relationship with demographic characteristics, school characteristics and labor market characteristics, and how these relationships have changed over the past decade.
The project name refers to the key focus of our study–student debt, in its many forms, sizes and payment schemes–but we are especially interested in the decisions leading up to and following debt take-up. These decisions include, for example, things that affect a person’s student debt load, like demographic characteristics, location, degree pursued, school attended; we also examine how this particular type of debt shapes individuals’ repayment behavior on other debt types, status and mobility in the labor market (such as those statistics from ADP’s Workforce Vitality Report), and social decisions like when to marry and where to live.
Additional research on the effects of institutional concentration on net tuition costs, as well as the relationship between federal/state funding and workforce trends, complement and contextualize our research on student debt.
Project leads: Laura Beamer, Marshall Steinbaum, Francis Tseng, and Eduard Nilaj.
Contact us about this project: jfi@jainfamilyinstitute.org
In This Series
Unequal and Uneven: The Geography of Higher Education Access
Declining Access, Rising Cost: The Geography of Higher Education Post-2008
Unceasing Debt, Disparate Burdens: Student Debt and Young America
Congressional Overlay
The Student Debt Crisis Is a Crisis of (Non-)Repayment
Student Debt and Young America Annual Report and Comparison Tool
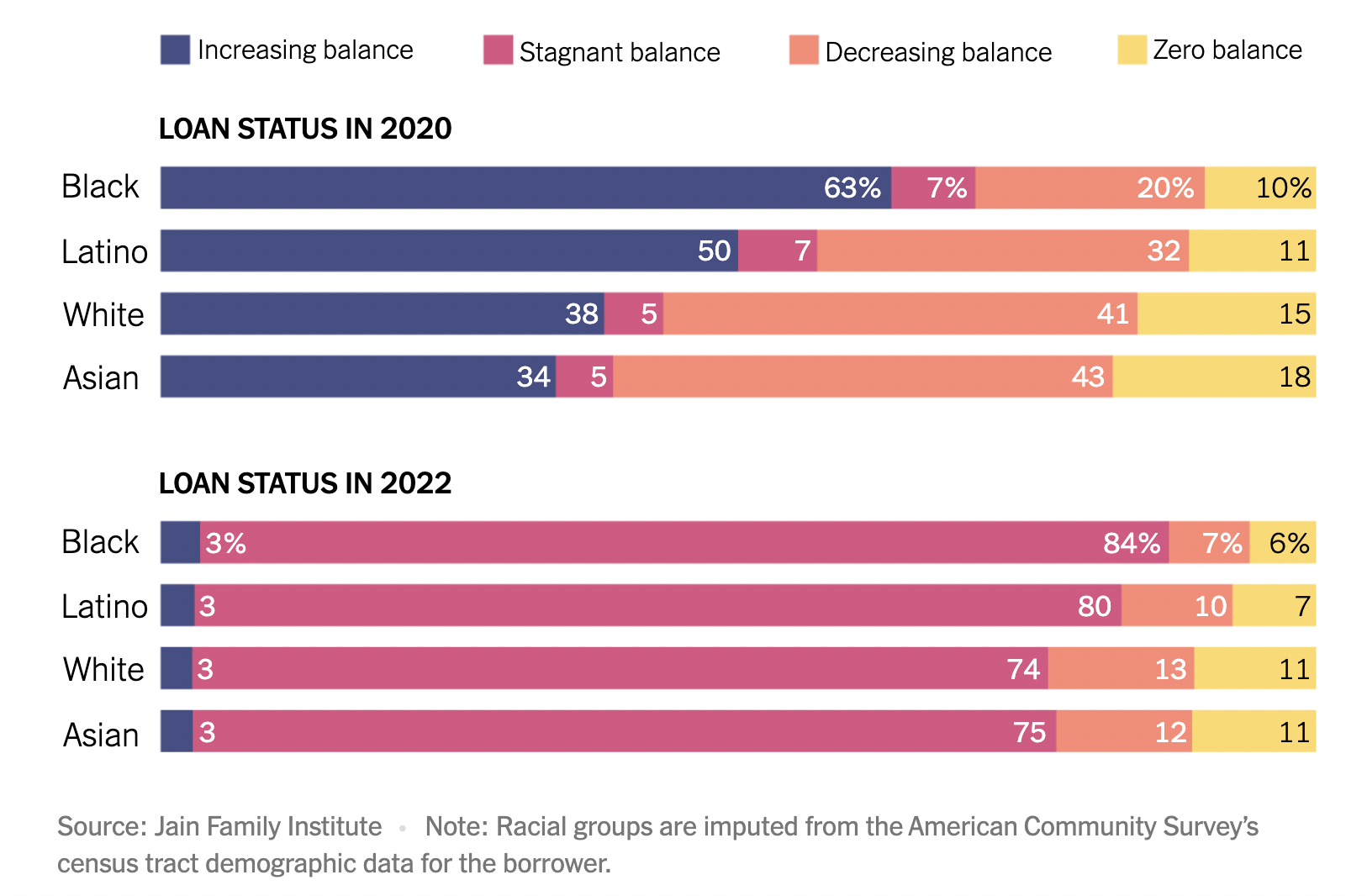
Student loans, the racial wealth divide, and why we need full student debt cancellation
Hysteresis and Student Debt
How Schools Lie: The Deceptive Financial Aid System at America’s Colleges
Homeownership and the Student Debt Crisis
Rules, Accountability, and the Student Debt Crisis
The Distribution of Student Debtors: Data, Narrative, and Debt Cancellation
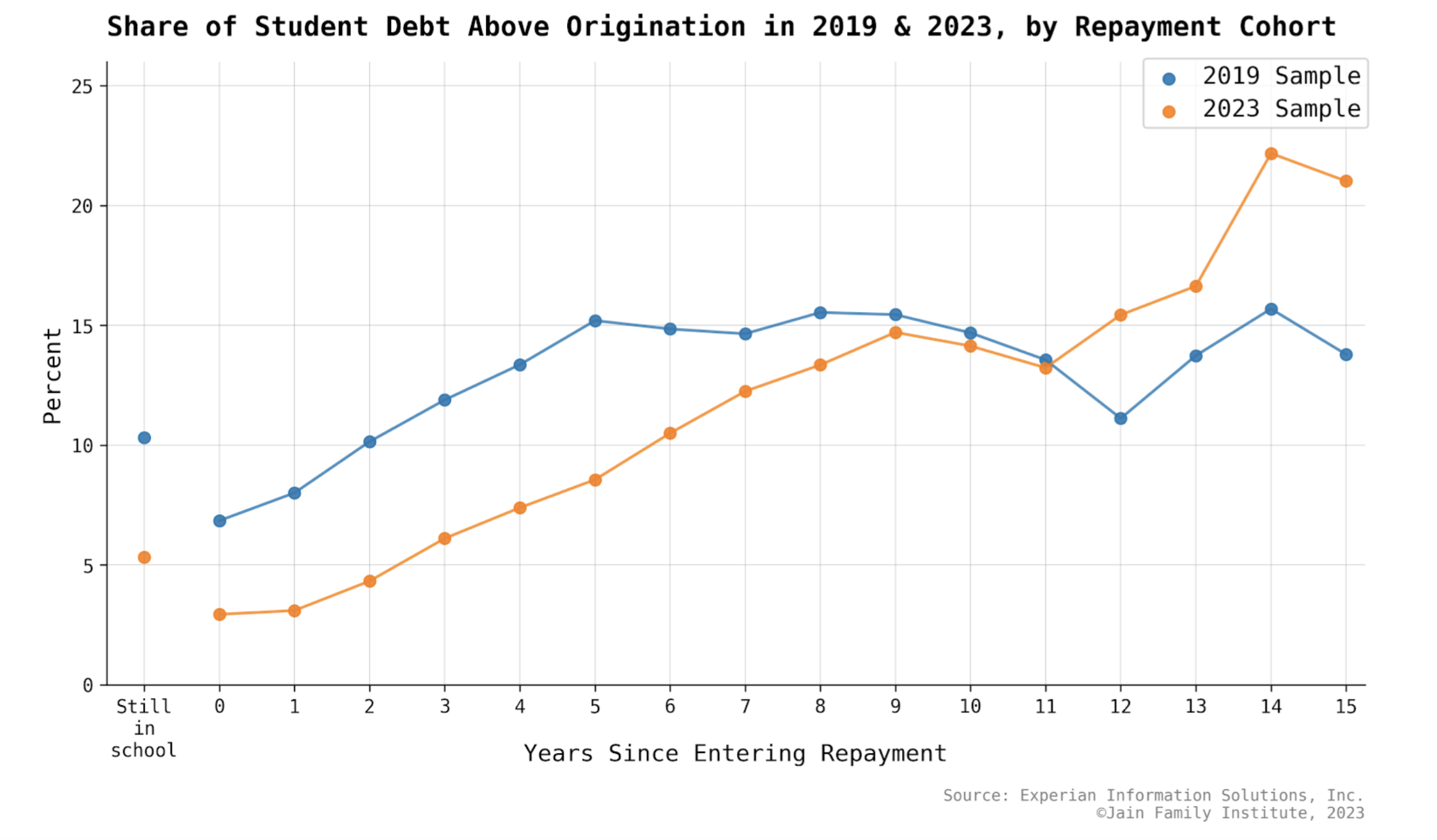
Student Debt and Young America in 2022 – Annual Report and Data Comparison Tool
The Repayment Pause and the Continuing Crisis of Non-Repayment
Student Debt and Homeownership Barriers in Washington, D.C.
Student Debt Relief for Borrowers with Negative Amortization
The Right Way to Cancel Student Debt
Cost Deception at Elite Private Colleges
A First Look at Student Debt Cancellation
New York Times Opinion: America’s Student Loans Were Never Going to Be Repaid
An interactive exploration of our Millennial Student Debt findings by Laura Beamer and Marshall Steinbaum, published July 2023.
Millennial Student Debt Contributors

Eduard Nilaj
Senior Research Associate

Laura Beamer
Lead Researcher

Marshall Steinbaum
Senior Fellow
Recent Updates
New Report on Student Debt Cancellation; Coverage in Marketwatch
Marketwatch: "The analysis is the first to provide a sense of who has benefited from the $153 billion in debt cancellation...
New Research in Millennial Student Debt: Relief for Borrowers with Negative Amortization
JFI's Higher Education Finance team publishes the first installment of part 14 of their flagship Millennial Student Debt research series.
Press Release: Student Debt and Homeownership Barriers in Washington, D.C.
A new collaborative report from the Jain Family Institute (JFI) and the Economic Policy Institute (EPI) sheds light on the...
Laura Beamer and Marshall Steinbaum publish editorial in the New York Times
"America's Student Loans Were Never Going to Be Repaid."
JFI’s Higher Education Finance research in The Guardian
Eduard Nilaj spoke to the Guardian after the Supreme Court's ruling against debt cancellation.
JFI’s Millennial Student Debt work widely covered in media
In light of a Supreme Court decision and the end of the repayment moratorium, coverage in Boston Globe, Forbes, Al-Jazeera,...
Fortune covers Millennial Student Debt research
On the resumption of federal student loan payments in October.
The New York Times covers JFI’s latest Millennial Student Debt report
On the upcoming end of a pandemic-era policy that has greatly benefitted student borrowers: the student loan repayment pause.
New Research in Millennial Student Debt: The Repayment Pause and the Continuing Crisis of Non-Repayment
JFI's Higher Education Finance team finds striking positive effects of the pandemic-era student loan repayment pause.
Forum on Education Deserts: Supporting Rural Regions With Fewer Colleges
On May 23, The Chronicle of Higher Education hosts a forum featuring JFI's Laura Beamer on higher education deserts in the...
Eduard Nilaj’s higher education analysis in Supreme Court amicus brief
Nilaj's work from Millennial Student Debt was cited by student loan experts.
Coverage of Millennial Student Debt
Marketwatch, Fortune, and Bloomberg covered our recent releases on the student debt crisis.
New Release: JFI’s Annual Student Debt Report, 2022
The 2022 "Student Debt and Young America" annual report shows a continued debt crisis but promising trends during three years of...
New Student Debt Report Compares Debtor Makeup to Narratives on Debt Cancellation
The tenth installment in the ongoing Millennial Student Debt project, Laura Beamer's newest report combines three datasets to analyze debt...
Research by Laura Beamer and Eduard Nilaj in the New York Times
JFI's higher ed research cited by David Brooks
Rules, Accountability, and the Student Debt Crisis – New report from Laura Beamer
The paper explores the cross-section of the student debt crisis and key accountability measures under discussion in the Dept. of...
Coverage of “Homeownership and Student Debt” in Bloomberg, Politico
"Homeownership and Student Debt" is the eighth post in JFI's Millennial Student Debt project
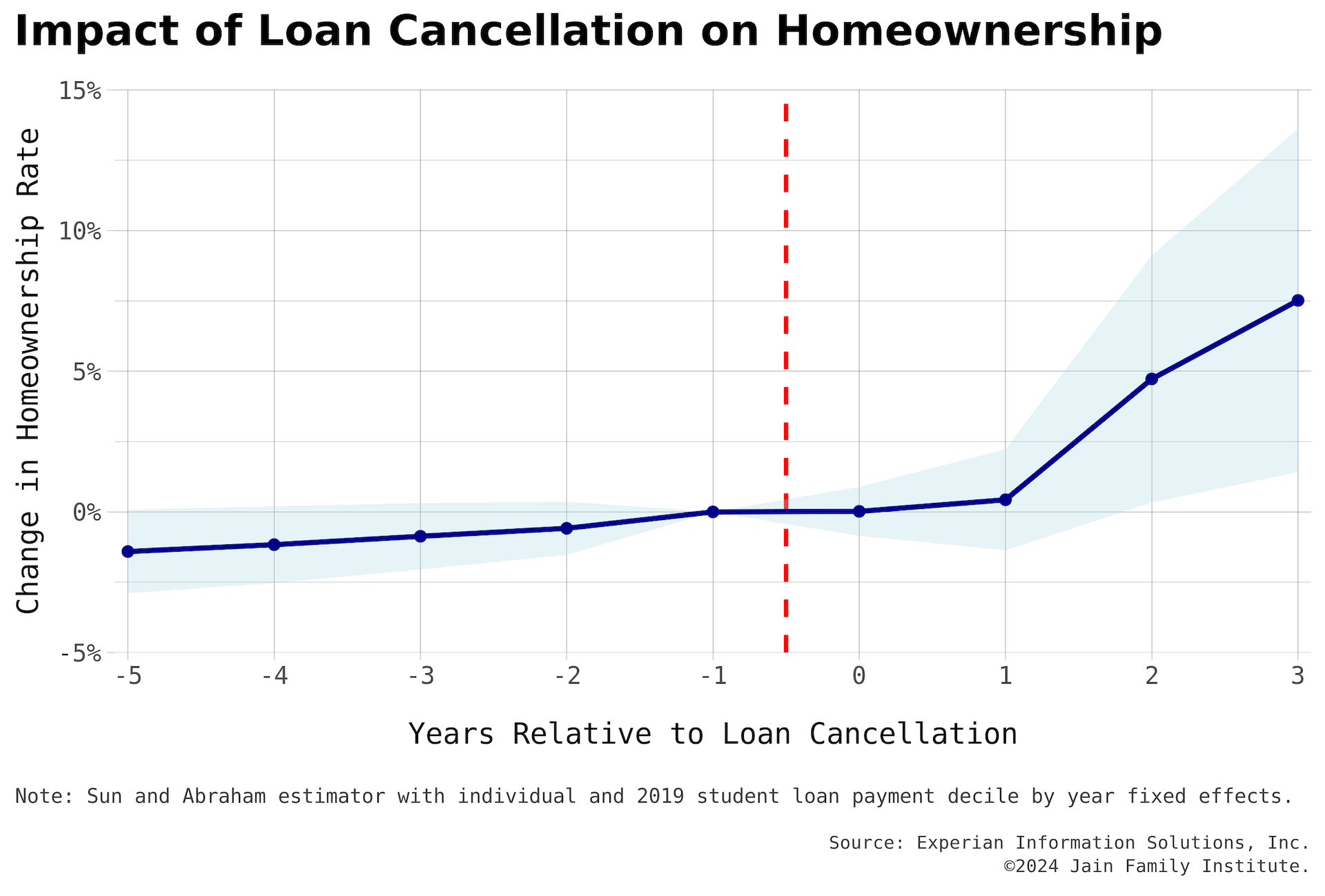
Homeownership and the Student Debt Crisis: Latest research from the Millennial Student Debt project
The eighth report in JFI’s student debt project, the research explores links between rising student debt and declining homeownership...
New Research in Millennial Student Debt: How Schools Lie
In "How Schools Lie: The Deceptive Financial Aid System at America's Colleges," JFI researchers explore how higher education institutions mislead...
New Publication: The Right Way to Cancel Student Debt
A data-driven case for universal, automatic, and generous debt cancellation.
Millennial Student Debt in Newsweek and NPR
Laura Beamer, Lead Researcher on Higher Education Finance, speaks about the student debt crisis
Student Debt and Young America: JFI’s annual report and new geographic comparison tool
The new report summarizes the state of student debt for 18 to 35 year olds; the accompanying comparison tool facilitates comparisons across...
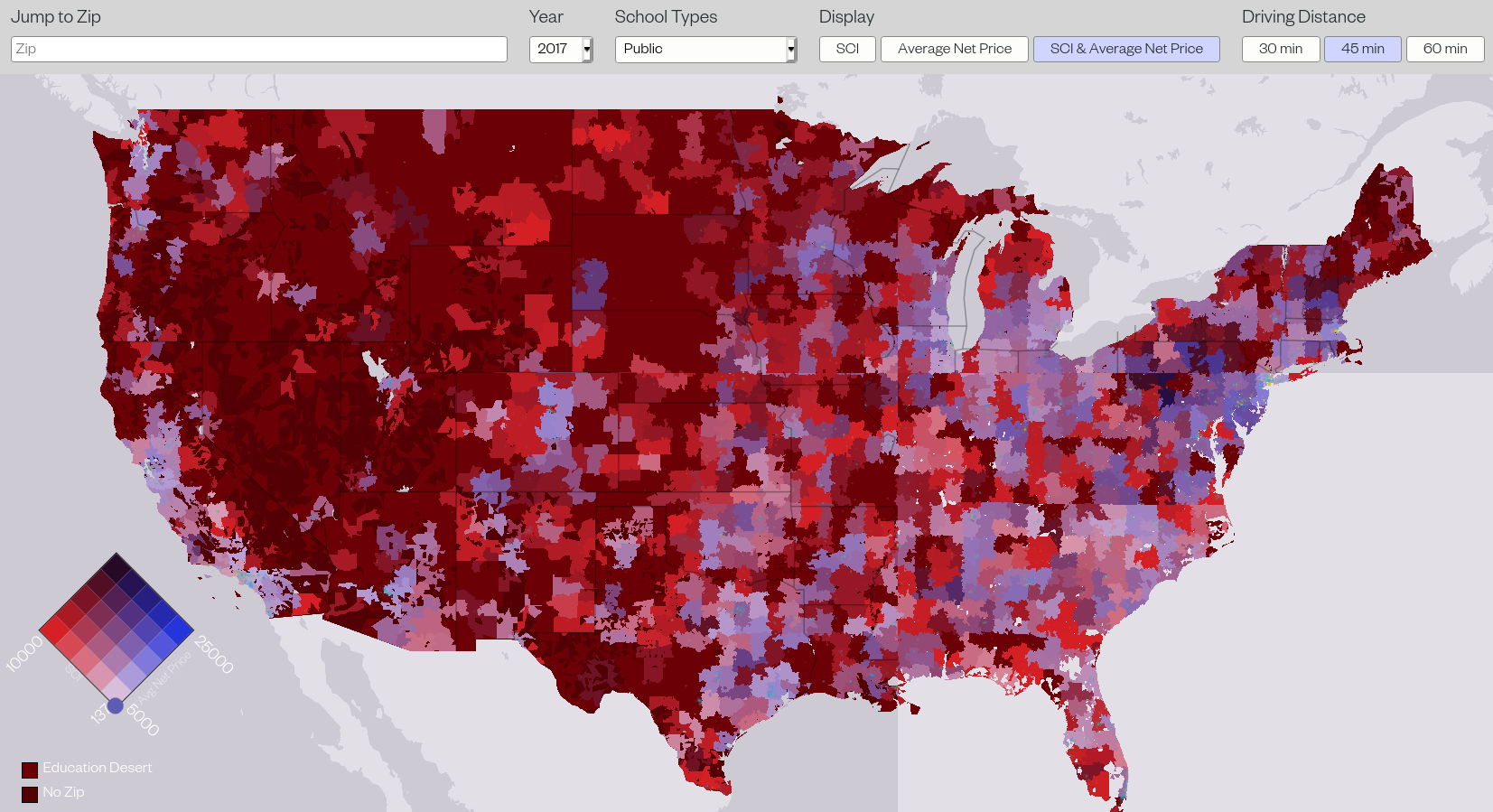
Millennial Student Debt maps win Dignity+Debt data visualization contest
Francis Tseng's maps show the geography of student debt across the United States
JFI releases map of student debt disparities across congressional districts, states
Following last week’s release of student debt trends since 2009, JFI provides a comprehensive tool for congressional advocacy on the...